Introduction
Real-time LiDAR annotation is at the cutting edge of technology, driving rapid advancements in various industries. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology provides critical spatial data that can be transformed into actionable insights through the process of annotation. As industries increasingly demand real-time decision-making, LiDAR annotation has emerged as a core component in applications like autonomous driving, smart cities, and real-time environmental monitoring.
This blog explores the significance of real-time LiDAR annotation for live applications, the industries it impacts, the challenges faced, current tools and technologies, and future trends that will shape its evolution.
Understanding Real-Time LiDAR Annotation
1.1 What is LiDAR?
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a technology that measures distances using laser light to generate precise, 3D representations of an environment. LiDAR sensors can capture millions of data points in the form of point clouds, representing objects, structures, and terrain. When processed, these point clouds offer a high level of detail for mapping and analysis.
LiDAR technology has been widely adopted for applications in various industries, ranging from urban planning and infrastructure monitoring to autonomous vehicles and robotics. However, raw LiDAR data alone is not sufficient for these applications—it needs to be processed and annotated for systems to make sense of it.
1.2 The Role of Annotation
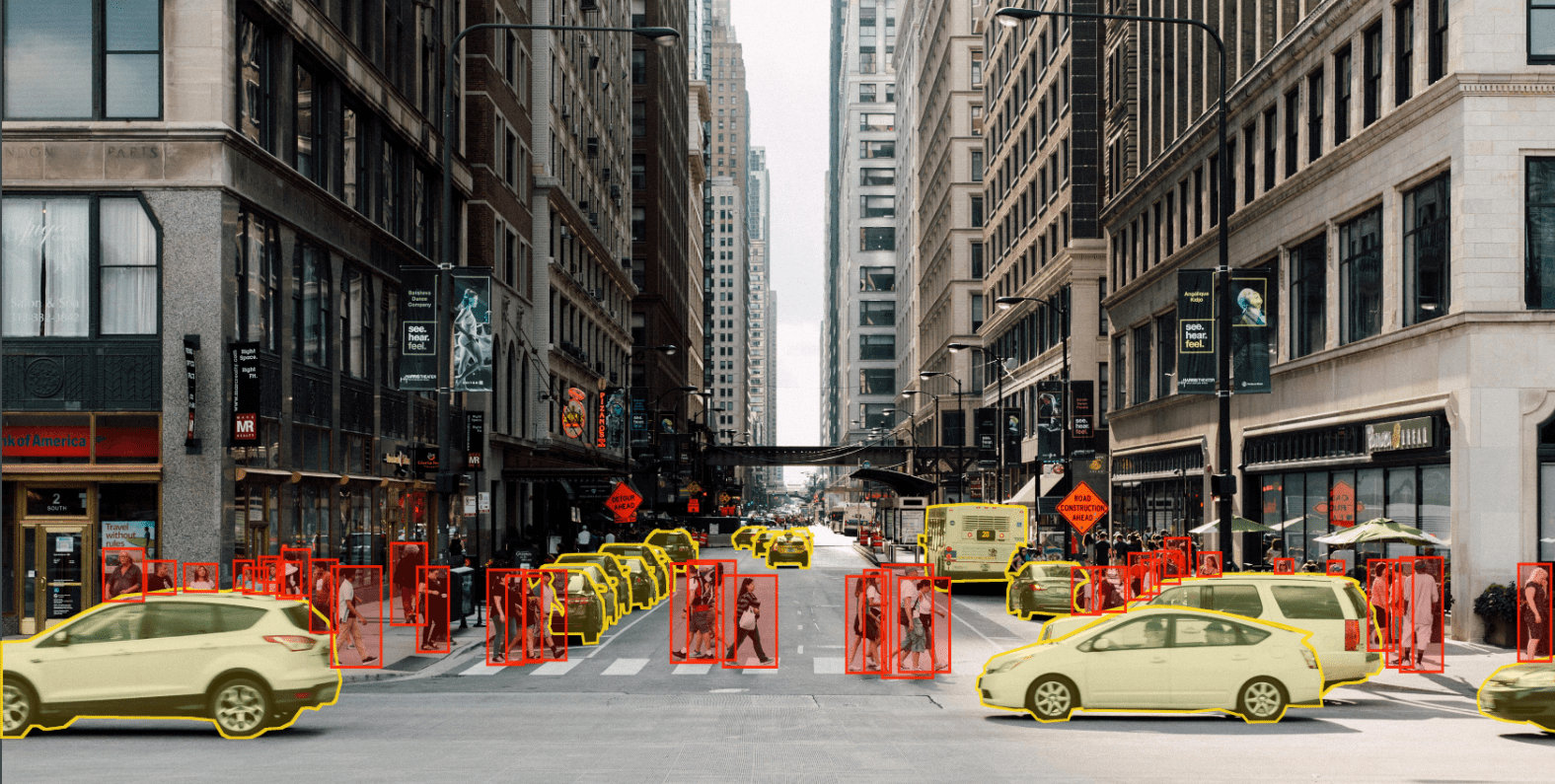
Annotation refers to the labeling or classification of objects within LiDAR data. In real-time applications, this process involves instant categorization of the data as it is captured by the sensor. For example, in an autonomous vehicle, the system must be able to recognize pedestrians, vehicles, and obstacles in real time to navigate safely.
Real-time annotation enables systems to extract meaning from raw data, allowing machine learning models and AI systems to make informed decisions. Without annotation, LiDAR data is simply a collection of points with no contextual information.
1.3 Why Real-Time Annotation Matters
In industries where time is critical, such as autonomous driving or dynamic traffic management, the ability to process and annotate data in real time is essential. Real-time annotation means that systems can make immediate decisions based on incoming data without delays. For example, in an autonomous vehicle, detecting a pedestrian crossing the road in real-time allows the system to react instantly to prevent accidents.
Real-time annotation is also crucial in other fields, such as urban planning, where continuous monitoring of infrastructure projects and construction sites can be enhanced through instant insights from annotated LiDAR data.
Key Applications of Real-Time LiDAR Annotation
Real-time LiDAR annotation has a wide range of applications in various industries. Here are some key sectors where real-time LiDAR annotation is transforming the way data is used.
2.1 Autonomous Vehicles
The most well-known application of real-time LiDAR annotation is in the development of autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars rely on LiDAR to create 3D maps of their environment and make real-time decisions to navigate safely. Annotating objects like pedestrians, vehicles, road signs, and obstacles in real-time allows autonomous vehicles to react instantly to changing conditions on the road.
In this context, real-time LiDAR annotation is used for:
- Object Detection: Detecting and classifying objects like vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, and obstacles.
- Path Planning: Mapping out a safe and efficient route based on annotated environmental data.
- Collision Avoidance: Predicting the movements of nearby objects and adjusting the vehicle’s trajectory to avoid collisions.
2.2 Smart Traffic Management
Smart cities are adopting real-time LiDAR systems to optimize traffic flow and manage urban transportation networks. Real-time annotation helps identify and classify vehicles, pedestrians, and other road users, enabling dynamic traffic management systems to adjust traffic signals, reroute vehicles, and prevent congestion.
Key benefits of real-time annotation in traffic management include:
- Vehicle and Pedestrian Detection: Monitoring traffic patterns and pedestrian crossings for safety.
- Dynamic Traffic Control: Optimizing traffic signal timings and rerouting vehicles in real time to reduce congestion.
- Incident Detection: Identifying accidents or unusual traffic patterns to dispatch emergency services promptly.
2.3 Robotics and Drones
LiDAR-equipped robots and drones are increasingly used in industries like logistics, construction, and agriculture. These machines rely on real-time LiDAR annotation to navigate complex environments, detect obstacles, and perform tasks autonomously.
For example, drones equipped with LiDAR sensors can be used to monitor construction sites, inspect infrastructure, and map large areas in real time. Annotated LiDAR data enables these drones to identify objects and structures accurately, allowing them to make informed decisions during flight.
2.4 Urban Planning and Infrastructure Monitoring
Real-time LiDAR annotation is revolutionizing the way cities are planned and managed. City planners and engineers use LiDAR data to monitor infrastructure projects, update maps, and inspect structures in real time. Annotated data helps them identify potential issues and make informed decisions about the future of urban development.
For example, real-time LiDAR annotation can be used to:
- Monitor Construction Sites: Track progress on infrastructure projects and detect potential safety hazards.
- 3D Mapping: Create detailed, up-to-date maps of urban environments for planning and development.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Identify defects or weaknesses in buildings, bridges, and other structures to enable timely repairs.
2.5 Environmental Monitoring
LiDAR technology is also used for environmental monitoring, helping researchers track changes in landscapes, forests, and coastlines. Real-time LiDAR annotation allows for immediate analysis of environmental data, enabling quick responses to natural disasters, deforestation, or erosion.
For example, drones equipped with LiDAR sensors can monitor forests for illegal logging or assess the impact of natural disasters on ecosystems. Annotated LiDAR data provides researchers with the information they need to take action in real time.
Challenges in Real-Time LiDAR Annotation
While real-time LiDAR annotation offers significant benefits, it also presents several challenges that must be addressed to achieve accurate and efficient results.
3.1 High Data Volume
LiDAR sensors generate massive amounts of point cloud data, which can be difficult to process in real time. A single LiDAR scan can capture millions of data points, and the need for continuous, high-speed processing adds to the complexity.
Processing this data in real time requires high-performance computing resources and optimized algorithms to ensure that systems can keep up with the flow of incoming data.
3.2 Computational Complexity
Annotating LiDAR data in real time is computationally intensive. Algorithms must quickly identify and classify objects within large datasets while maintaining high accuracy. This requires advanced hardware, such as GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), and sophisticated software capable of handling the computational load.
3.3 Accuracy vs. Speed Trade-Off
In real-time applications, there is often a trade-off between speed and accuracy. Systems need to process data quickly to make immediate decisions, but sacrificing accuracy can lead to mistakes, which could be dangerous in critical applications like autonomous driving.
Developers face the challenge of creating algorithms that can process data quickly without compromising the quality of the annotations.
3.4 Handling Environmental Factors
LiDAR systems are sensitive to environmental conditions such as rain, fog, and snow. These factors can affect the quality of the data and introduce noise or distortions. Real-time annotation systems must be robust enough to handle these conditions and accurately label objects even in poor visibility.
3.5 Edge Cases and Anomalies
In dynamic environments, real-time LiDAR systems must be prepared to handle unexpected scenarios or “edge cases.” These could include unusual objects, unpredictable movements, or sudden changes in the environment. Annotating these anomalies in real time requires advanced AI and machine learning models that can adapt to new situations quickly.
Tools and Technologies for Real-Time LiDAR Annotation
Several tools and platforms are available for real-time LiDAR annotation, each offering different features and capabilities. Here are some of the most widely used tools in the industry.
SO Development:
SO Development offers cutting-edge solutions for real-time LiDAR annotation, designed for live applications in industries like autonomous driving, urban planning, and environmental monitoring. Their platform combines AI-driven automation with manual oversight to ensure high-quality annotation at scale. SO Development’s real-time processing capabilities allow for instant data interpretation and decision-making, making it ideal for fast-paced, dynamic environments.

Labelbox
Labelbox is a popular platform that provides tools for real-time LiDAR data annotation. It supports 3D point cloud data and offers collaboration options, making it suitable for large-scale annotation projects. Labelbox also integrates AI-assisted annotation features, helping users speed up the labeling process while maintaining accuracy.

Supervisely
Supervisely is a cloud-based platform designed for real-time LiDAR annotation, particularly for applications in autonomous vehicles and robotics. It provides tools for 3D point cloud labeling and integrates machine learning models to assist with object detection and classification in real time. The platform also allows for collaborative annotation workflows, making it easier for teams to work together on large datasets.

Scale AI
Scale AI offers a range of services for real-time LiDAR annotation, with a focus on applications in autonomous vehicles and smart cities. The platform provides AI-driven automation for point cloud annotation, helping users process large datasets quickly and accurately. Scale AI also offers quality control features to ensure that annotated data meets the highest standards.

AI and Machine Learning in Real-Time LiDAR Annotation
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing a significant role in automating the real-time annotation of LiDAR data. By training models to recognize and label objects in point clouds, AI-driven systems can significantly speed up the annotation process while maintaining accuracy.
5.1 AI-Driven Automation
AI-driven automation is transforming the way real-time LiDAR annotation is performed. Machine learning models are trained to detect and classify objects within point cloud data, reducing the need for manual annotation. This not only speeds up the process but also improves accuracy by minimizing human error.
- Object Detection and Segmentation: AI models can be trained to detect and segment objects in real-time, allowing for instant annotation of vehicles, pedestrians, and other road users.
- Model Training with LiDAR Data: Machine learning models rely on annotated data to learn how to recognize and classify objects. Real-time annotation provides immediate feedback to these models, enabling continuous improvement.
5.2 Active Learning
Active learning is a machine learning approach that allows models to improve their accuracy by selecting the most informative data points for annotation. In real-time LiDAR annotation, active learning can be used to prioritize the annotation of challenging or uncertain objects, ensuring that the most important data is processed first.
5.3 AI-Enhanced Accuracy
AI-driven systems can achieve higher levels of accuracy in real-time annotation by continuously learning from annotated data. As models are exposed to more data, they become better at detecting and classifying objects, reducing the chances of errors in real-time applications.
Conclusion
Real-time LiDAR annotation is a transformative technology that is enabling faster, more accurate decision-making across a wide range of industries. From autonomous vehicles to smart cities, real-time annotation provides the critical insights needed to navigate dynamic environments and optimize operations.
As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, the future of real-time LiDAR annotation looks even more promising. Advanced algorithms, improved hardware, and smarter AI models will further enhance the capabilities of LiDAR systems, allowing for even greater accuracy and efficiency in real-time applications.