Introduction Edge AI is transforming how computer vision systems are deployed, moving intelligence from the cloud directly onto devices operating in real time. NVIDIA Jetson platforms make this possible by combining GPU acceleration, low power consumption, and optimized AI software stacks. With the latest Ultralytics YOLO26 model, developers can achieve faster inference, improved detection accuracy, and efficient deployment on embedded systems. When combined with NVIDIA DeepStream SDK and TensorRT optimization, YOLO26 becomes a powerful solution for real-time video analytics at the edge. This guide walks through end-to-end integration of YOLO26 with DeepStream on Jetson, enabling scalable, production-ready object detection pipelines. Why DeepStream for Edge AI? Running raw inference scripts works for experimentation, but production deployments require: High-throughput video processing Hardware acceleration Multi-stream scalability Efficient memory handling Pipeline-based architecture DeepStream provides: ✅ GPU-accelerated video decoding✅ Zero-copy memory pipelines✅ Batch inference support✅ Built-in tracking and analytics✅ RTSP and camera streaming support Instead of processing frames manually, DeepStream builds optimized pipelines using GStreamer. System Architecture Overview The deployment stack looks like this: Camera / Video Stream ↓ Video Decode (NVDEC) ↓ DeepStream Pipeline ↓ TensorRT Engine (YOLO26) ↓ Object Detection Metadata ↓ Display / Stream / Analytics Key components: Component Purpose YOLO26 Object detection model TensorRT Optimized inference engine DeepStream Video analytics pipeline Jetson GPU Hardware acceleration Hardware Requirements Supported Jetson platforms: Jetson Nano (limited performance) Jetson Xavier NX Jetson AGX Xavier Jetson Orin Nano Jetson Orin NX Jetson AGX Orin (recommended) Recommended minimum: 8GB RAM JetPack 6.x CUDA + TensorRT installed Software Stack Ensure the following are installed: JetPack SDK CUDA Toolkit TensorRT DeepStream SDK Python 3.8+ Ultralytics framework Verify installation: deepstream-app –version-all Step 1 — Install Ultralytics YOLO26 Clone and install dependencies: pip install ultralytics Test inference: yolo predict model=yolo26.pt source=bus.jpg If inference works, proceed to export. Step 2 — Export YOLO26 to ONNX DeepStream uses TensorRT engines, so first export the model. yolo export model=yolo26.pt format=onnx opset=12 Output: yolo26.onnx Verify ONNX model: pip install onnxruntime python -c "import onnx; onnx.load('yolo26.onnx')" Step 3 — Convert ONNX to TensorRT Engine Use TensorRT to optimize inference for Jetson GPU. /usr/src/tensorrt/bin/trtexec –onnx=yolo26.onnx –saveEngine=yolo26.engine –fp16 Optional INT8 optimization (advanced): –int8 –calib=calibration.cache Benefits: Lower latency Reduced memory usage Hardware-specific optimization Step 4 — Integrate YOLO26 with DeepStream DeepStream requires a custom parser for YOLO outputs. Directory Structure deepstream_yolo26/ ├── config_infer_primary.txt ├── yolo26.engine ├── labels.txt └── custom_parser.cpp Configure Primary Inference Create: config_infer_primary.txt [property] gpu-id=0 net-scale-factor=0.003921569 model-engine-file=yolo26.engine labelfile-path=labels.txt batch-size=1 network-mode=2 num-detected-classes=80 process-mode=1 gie-unique-id=1 Network modes: 0 → FP32 1 → INT8 2 → FP16 Custom Bounding Box Parser YOLO models output tensors differently from standard detectors.You must implement a parser that converts raw outputs into: bounding boxes class IDs confidence scores Compile parser: make Output: LZ4ezwuSpTeD9pQKcUaPpHYUhy53QerXiD Step 5 — Modify DeepStream App Config Edit: deepstream_app_config.txt Set primary inference: [primary-gie] enable=1 config-file=config_infer_primary.txt Step 6 — Run DeepStream Pipeline Launch: deepstream-app -c deepstream_app_config.txt You should see: ✅ Real-time detections✅ Bounding boxes rendered✅ GPU utilization active Performance Optimization Tips 1. Use FP16 or INT8 FP16 typically provides: 2–3× faster inference Minimal accuracy loss INT8 gives maximum performance but requires calibration. 2. Increase Batch Size (Multi-Stream) batch-size=4 Useful for multiple RTSP cameras. 3. Enable Zero-Copy Memory DeepStream automatically uses NVMM buffers to avoid CPU copies. 4. Use Hardware Decoder Ensure pipeline uses: nvv4l2decoder instead of software decoding. Expected Performance (Approximate) Device FPS (YOLO26 FP16) Jetson Nano 6–10 FPS Xavier NX 25–40 FPS Orin Nano 40–70 FPS AGX Orin 90–150 FPS Performance varies with resolution and model size. Real-World Use Cases YOLO26 + DeepStream enables: Smart city surveillance Retail analytics Industrial safety monitoring Traffic analysis Robotics perception Autonomous inspection systems Troubleshooting Engine Not Loading Rebuild engine directly on Jetson: trtexec –onnx=model.onnx TensorRT engines are hardware-specific. No Bounding Boxes Appearing Check: parser library path class count output tensor names Low FPS Verify GPU usage: tegrastats Common causes: CPU decoding FP32 inference incorrect batch configuration Best Practices for Production Build TensorRT engines on target hardware Use RTSP streams for scalability Enable tracking plugins Log inference metadata Containerize with Docker Conclusion Integrating YOLO26 with DeepStream on NVIDIA Jetson unlocks a highly optimized edge AI pipeline capable of real-time video analytics at production scale. By combining: YOLO26 detection accuracy TensorRT acceleration DeepStream pipeline efficiency Jetson edge hardware developers can deploy scalable, low-latency AI systems without relying on cloud infrastructure. This workflow forms a strong foundation for next-generation edge vision applications across industries. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now
Introduction Artificial intelligence is getting bigger every year. Modern Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama, Qwen, and GPT-style models often contain tens of billions of parameters, usually requiring expensive GPUs with massive VRAM. For most developers, startups, and researchers, running these models locally feels impossible. But a new tool called oLLM is quietly changing that. Imagine running models as large as 80B parameters on a consumer GPU with just 8GB of VRAM. Sounds unrealistic, right? Yet that’s exactly what oLLM enables through clever engineering and smart memory management. In this article, we’ll explore what oLLM is, how it works, and why it may become the secret ingredient for running massive AI models on tiny hardware. What is oLLM? oLLM is a lightweight Python library designed for large-context LLM inference on resource-limited hardware. It builds on top of popular frameworks like Hugging Face Transformers and PyTorch, allowing developers to run large AI models locally without requiring enterprise-grade GPUs. The key idea behind oLLM is simple: Instead of forcing everything into GPU memory, intelligently move parts of the model to other storage layers. With this approach, models that normally need hundreds of gigabytes of VRAM can run on standard consumer hardware. For example, some setups allow models such as: Llama-3 style models GPT-OSS-20B Qwen-Next-80B to run on a machine with only 8GB GPU VRAM plus SSD storage. The Problem with Running Large AI Models Traditional AI inference assumes one thing: All model weights must fit inside GPU memory. This becomes a huge bottleneck because: Model Size Typical VRAM Needed 7B ~16 GB 13B ~24 GB 70B ~140 GB 80B ~190 GB Clearly, that’s far beyond what most consumer GPUs can handle. Even developers with powerful GPUs often rely on quantization, which compresses model weights to reduce memory usage. But quantization comes with trade-offs: Reduced accuracy Lower output quality Compatibility limitations oLLM takes a different approach. The Core Innovation: SSD Offloading The breakthrough behind oLLM is SSD-based memory offloading. Instead of loading the entire model into GPU memory, oLLM streams model components dynamically between: GPU VRAM System RAM High-speed SSD This means your GPU only holds the active parts of the model at any given time. The technique allows models to run that are 10x larger than the available GPU memory. Think of it like this: Traditional AI Model → GPU VRAM oLLM Model → SSD + RAM + GPU (streamed dynamically) By turning storage into an extension of GPU memory, oLLM bypasses the biggest limitation in local AI development. No Quantization Needed Another major advantage of oLLM is that it does not require quantization. Instead of compressing model weights, it keeps them in high precision formats such as FP16 or BF16, preserving the original model quality. That means: Better reasoning quality More accurate outputs More reliable responses For developers working on research, compliance analysis, or long-document reasoning, this can make a huge difference. Ultra-Long Context Windows Many AI tools struggle with large documents because of context limits. oLLM supports extremely long context windows — up to 100,000 tokens. This allows the model to process: Entire books Long research papers Legal contracts Massive log files Large datasets —all in a single prompt. This opens the door for advanced offline tasks like: document intelligence compliance auditing enterprise knowledge search AI-assisted research Performance Trade-offs Of course, running massive models on small hardware has trade-offs. Since parts of the model are constantly streamed from storage, speed can be slower than running everything in VRAM. For example: Large models may generate around 0.5 tokens per second on consumer GPUs. That might sound slow, but it’s perfectly acceptable for offline workloads, such as: document analysis research tasks batch processing AI pipelines In many cases, cost savings outweigh the speed limitations. Multimodal Capabilities oLLM is not limited to text models. It can also support multimodal AI systems, including models that process: text + audio text + images Examples include models like: Voxtral-Small-24B (audio + text) Gemma-3-12B (image + text) This allows developers to build advanced AI applications that combine multiple data types. Why oLLM Matters for the Future of AI AI is currently dominated by cloud infrastructure and billion-dollar GPU clusters. But tools like oLLM represent a shift toward democratized AI infrastructure. Instead of needing: expensive GPUs massive cloud budgets specialized infrastructure developers can experiment with powerful models on regular hardware. This unlocks new opportunities for: indie developers startups academic researchers privacy-focused applications Local AI and Privacy Running AI locally also has a major benefit: privacy. When models run on your own machine: no data leaves your system no prompts are logged sensitive documents remain private This is especially valuable for industries like: healthcare finance legal services government Use Cases for oLLM Some real-world applications include: Research assistants Analyze entire research papers or datasets locally. Legal document analysis Process massive contracts and legal records with long context windows. Offline AI pipelines Run batch inference jobs without relying on cloud services. Privacy-focused AI tools Keep sensitive data completely local. Developer experimentation Test large models without investing in expensive hardware. Limitations to Know While impressive, oLLM isn’t perfect. Current limitations include: Slower inference compared to full-VRAM setups Heavy SSD usage Limited compatibility with some hardware (like certain Apple Silicon setups) However, these are common trade-offs in early infrastructure tools. As storage speeds and optimization techniques improve, performance will likely get better. The Bigger Trend: AI on Everyday Devices oLLM is part of a larger shift toward local AI computing. We are moving from: Cloud-only AI → Hybrid AI → Fully local AI Future devices may run powerful AI models directly on: laptops smartphones edge devices IoT hardware This transformation will make AI more accessible, private, and decentralized. Final Thoughts oLLM proves something important: You don’t always need a $10,000 GPU server to run powerful AI. Through clever memory management, SSD streaming, and high-precision inference, oLLM enables developers to run massive AI models on surprisingly small hardware. For AI enthusiasts, researchers, and builders, this is an exciting step toward a future
Introduction For nearly a decade, the YOLO (You Only Look Once) family has defined what real-time computer vision means. From the revolutionary YOLOv1 in 2015 to increasingly efficient and accurate successors, each generation has pushed the boundary between speed, accuracy, and deployability. In 2026, a new milestone arrived. YOLO26 is not just another incremental upgrade, it represents a fundamental redesign of how object detection systems are trained, optimized, and deployed, especially for edge devices and real-world AI systems. Built with an edge-first philosophy, YOLO26 introduces end-to-end detection without traditional post-processing, improved stability during training, and multi-task vision capabilities, making it one of the most practical computer vision models ever released. This article explores: ✅ The evolution leading to YOLO26✅ Architecture innovations✅ Why NMS-free detection matters✅ Performance improvements✅ Real-world applications✅ How developers can use YOLO26 today✅ The future of vision AI The Journey to YOLO26 Object detection historically struggled with a difficult trade-off: Faster models sacrificed accuracy Accurate models required heavy computation Real-time deployment remained difficult Earlier YOLO versions gradually solved these problems: YOLOv5–v8 improved usability and modular training YOLOv9–v11 introduced smarter gradient learning and efficiency improvements YOLOv10 began moving toward end-to-end detection pipelines YOLO26 completes this transition. Instead of patching limitations with additional heuristics, it redesigns the pipeline itself. Research analyzing the model highlights that YOLO26 establishes a new efficiency–accuracy balance while outperforming many previous detectors in both speed and precision. What Is YOLO26? YOLO26 is a real-time, multi-task computer vision model optimized for: Object detection Instance segmentation Pose estimation Tracking Classification Unlike earlier detectors, YOLO26 is designed primarily for edge deployment, meaning it runs efficiently on: CPUs Mobile devices Embedded systems Robotics hardware Jetson and ARM platforms The model supports scalable sizes, allowing developers to choose between lightweight and high-accuracy configurations depending on hardware constraints. The Biggest Breakthrough: NMS-Free Detection The Problem with Traditional YOLO Previous YOLO models relied on Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). NMS removes duplicate bounding boxes after prediction — but it introduces problems: Extra latency Hyperparameter tuning complexity Instability in crowded scenes Deployment inconsistencies YOLO26 Solution YOLO26 eliminates NMS entirely. Instead, detection becomes fully end-to-end — predictions are learned directly during training rather than filtered afterward. This change: Reduces inference time Simplifies deployment Improves consistency across devices Researchers note that removing heuristic post-processing resolves long-standing latency vs. precision trade-offs in object detection systems. Key Architectural Innovations YOLO26 introduces several new mechanisms. 1. Progressive Loss Balancing (ProgLoss) Training object detectors often suffers from unstable gradients. ProgLoss dynamically adjusts learning emphasis during training, allowing: Faster convergence Improved generalization Stable optimization on small datasets 2. Small-Target-Aware Label Assignment (STAL) Small objects are traditionally difficult to detect. STAL improves label assignment by prioritizing tiny and distant objects — critical for: Surveillance Drone imagery Autonomous driving Medical imaging 3. MuSGD Optimizer Inspired by optimization strategies used in large AI models, MuSGD improves: Training stability Quantization readiness Low-precision deployment 4. Removal of Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) Earlier YOLO versions used complex bounding box regression losses. YOLO26 simplifies this pipeline, enabling: Easier export to ONNX/TensorRT Faster inference Reduced memory overhead Where YOLOv1 Fell Short, and Why That’s Important YOLOv1’s limitations weren’t accidental; they revealed deep insights. Small Objects Grid resolution limited detection granularity Small objects often disappeared within grid cells Crowded Scenes One object class prediction per cell Overlapping objects confused the model Localization Precision Coarse bounding box predictions Lower IoU scores than region-based methods Each weakness became a research question that drove YOLOv2, YOLOv3, and beyond. Edge-First Design Philosophy One of YOLO26’s defining goals is predictable latency. Traditional models were GPU-centric. YOLO26 focuses on: CPU acceleration Embedded inference Low-power AI devices Benchmarks show significant CPU inference improvements and reliable performance even without GPUs. This shift makes AI accessible beyond data centers. Performance Improvements YOLO26 improves across three critical axes: Speed Faster inference due to NMS removal Reduced computational overhead Accuracy Better small-object detection Improved dense-scene performance Efficiency Smaller models with higher mAP Stable quantization for edge deployment Studies comparing YOLO26 with earlier generations highlight superior deployment versatility and efficiency across edge hardware platforms. Multi-Task Vision: One Model, Many Tasks YOLO26 moves toward unified vision AI. Supported tasks include: Detection Segmentation Pose estimation Tracking Oriented bounding boxes This reduces the need to maintain separate models for each task, simplifying production pipelines. Real-World Applications YOLO26 unlocks new possibilities across industries. Autonomous Systems Robots navigating dynamic environments Drone inspection systems Smart Cities Traffic monitoring Crowd analysis Security automation Healthcare Real-time medical imaging assistance Surgical instrument tracking Manufacturing Defect detection Quality assurance automation Retail & Logistics Shelf analytics Warehouse automation Because it runs efficiently on edge devices, processing can happen locally — improving privacy and reducing cloud costs. Developer Experience One reason YOLO became dominant is usability — and YOLO26 continues that tradition. Developers benefit from: Simple training pipelines Export to multiple runtimes Easy fine-tuning Real-time video inference Typical workflow: Prepare dataset Train using pretrained weights Export model Deploy on edge device No complex post-processing configuration required. YOLO26 vs Previous YOLO Versions Feature YOLOv8–11 YOLO26 NMS Required Yes No Edge Optimization Moderate Native Multi-Task Support Partial Unified Training Stability Good Improved Deployment Complexity Medium Low YOLO26 marks the transition from fast detectors to deployment-ready AI systems. Challenges and Limitations Despite improvements, challenges remain: Dense overlapping scenes still difficult Training large datasets remains compute-heavy Open-vocabulary detection is limited Transformer integration still evolving Future models may combine YOLO efficiency with foundation-model reasoning. The Future After YOLO26 YOLO26 signals a broader shift in computer vision: 👉 From GPU-centric AI → Edge AI👉 From pipelines → End-to-end learning👉 From single-task → unified perception systems Future developments may include: Vision-language integration Self-supervised detection On-device continual learning Autonomous AI perception stacks Conclusion YOLO26 is more than a version update. It represents a philosophical shift in computer vision engineering — simplifying architecture while improving real-world performance. By removing legacy bottlenecks like NMS, introducing smarter training strategies, and prioritizing edge deployment, YOLO26 brings AI closer to where it matters most: the real world. As AI moves beyond research labs into everyday devices, models like
Introduction Higher education is entering one of the most transformative periods in its history. Just as the internet redefined access to knowledge and online learning reshaped classrooms, Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) is now redefining how knowledge is created, delivered, and consumed. Unlike traditional AI systems that analyze or classify data, Generative AI can produce new content — including text, code, images, simulations, and even research drafts. Tools powered by large language models are already assisting students with learning, supporting professors in course design, and accelerating academic research workflows. Universities worldwide are moving beyond experimentation. Generative AI is rapidly becoming an essential academic infrastructure — influencing pedagogy, administration, research, and institutional strategy. This article explores how Generative AI is transforming higher education, its opportunities and risks, and what institutions must do to adapt responsibly. What Is Generative AI? Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems capable of creating original outputs based on patterns learned from large datasets. These systems rely on advanced machine learning architectures such as: Large Language Models (LLMs) Diffusion models Transformer-based neural networks Multimodal AI systems Examples of generative outputs include: Essays and academic explanations Programming code Research summaries Visual diagrams Educational simulations Interactive tutoring conversations In higher education, this ability shifts AI from being a passive analytical tool into an active collaborator in learning and research. Personalized Learning at Scale One of the most powerful applications of Generative AI is personalized education. Traditional classrooms struggle to adapt to individual learning speeds and styles. AI-powered systems can now: Explain complex concepts in multiple ways Adjust difficulty dynamically Provide instant feedback Generate customized practice exercises Support multilingual learning A student struggling with calculus, for example, can receive step-by-step explanations tailored to their understanding level — something previously impossible at scale. Benefits for Students 24/7 academic assistance Reduced learning gaps Improved engagement Increased confidence in difficult subjects Generative AI effectively acts as a personal academic tutor available anytime. The Evolution of Technology in Higher Education To understand the impact of Generative AI, it helps to view it within the broader evolution of educational technology: Era Technology Impact Pre-2000 Digital libraries and basic computing 2000–2015 Learning Management Systems (LMS) and online courses 2015–2022 Data analytics and adaptive learning 2023–Present Generative AI and intelligent academic assistance While previous technologies improved access and efficiency, Generative AI changes something deeper — how knowledge itself is produced and understood. Empowering Educators, Not Replacing Them A common misconception is that AI will replace professors. In reality, Generative AI is emerging as a productivity amplifier. Educators can use AI to: Draft lecture materials Create quizzes and assignments Generate case studies Design simulations Summarize research papers Translate learning content This reduces administrative workload and allows instructors to focus on what matters most: Mentorship Critical discussion Research supervision Human-centered teaching The role of educators is shifting from information delivery toward learning facilitation and intellectual guidance. Revolutionizing Academic Research Research is another domain experiencing rapid transformation. Generative AI accelerates research workflows by helping scholars: Conduct literature reviews faster Summarize thousands of papers Generate hypotheses Assist with coding and data analysis Draft early manuscript versions For interdisciplinary research, AI can bridge knowledge gaps across domains, helping researchers explore unfamiliar fields more efficiently. However, AI-generated research must always be validated by human expertise to maintain academic integrity. AI-Assisted Writing and Academic Productivity Writing is central to higher education, and Generative AI has dramatically changed the writing process. Students and researchers now use AI tools for: Brainstorming ideas Structuring arguments Improving clarity and grammar Formatting citations Editing drafts When used responsibly, AI becomes a thinking partner, not a shortcut. Universities increasingly encourage transparent AI usage policies rather than outright bans. Administrative Transformation Beyond classrooms and research, Generative AI is reshaping university operations. Applications include: Automated student support chatbots Enrollment assistance Academic advising systems Curriculum planning analysis Predictive student success modeling Institutions can improve efficiency while providing faster and more personalized student services. Ethical Challenges and Academic Integrity Despite its benefits, Generative AI introduces serious challenges. Key Concerns Academic plagiarism Overreliance on AI-generated work Bias in training data Hallucinated information Data privacy risks Universities must rethink assessment methods. Instead of memorization-based exams, institutions are moving toward: Project-based learning Oral examinations Critical reasoning evaluation AI-assisted but transparent workflows The goal is not to eliminate AI usage but to teach responsible AI literacy. The Rise of AI Literacy as a Core Skill Just as digital literacy became essential in the early 2000s, AI literacy is becoming a foundational academic skill. Students must learn: How AI systems work When AI outputs are unreliable Ethical usage practices Prompt engineering Verification and fact-checking Future graduates will not compete against AI — they will compete against people who know how to use AI effectively. Challenges Universities Must Overcome Adopting Generative AI at scale requires addressing institutional barriers: Faculty training gaps Policy uncertainty Infrastructure costs Data governance concerns Resistance to change Universities that delay adaptation risk falling behind in global academic competitiveness. The Future of Higher Education with Generative AI Looking ahead, several trends are emerging: AI-native universities and curricula Fully personalized degree pathways Intelligent research assistants Multimodal learning environments AI-driven virtual laboratories Education may shift from standardized programs toward adaptive lifelong learning ecosystems. Best Practices for Responsible Adoption Institutions should consider: ✅ Clear AI usage guidelines✅ Faculty and student training programs✅ Transparent disclosure policies✅ Human oversight in assessment✅ Ethical AI governance frameworks Responsible adoption ensures innovation without compromising academic values. Conclusion Generative AI is not simply another educational technology trend — it represents a structural transformation in how higher education operates. By enabling personalized learning, accelerating research, empowering educators, and improving institutional efficiency, Generative AI has the potential to democratize knowledge at an unprecedented scale. The universities that succeed will not be those that resist AI, but those that integrate it thoughtfully, ethically, and strategically. Higher education is evolving from static knowledge delivery toward dynamic human-AI collaboration, preparing students for a future where creativity, critical thinking, and technological fluency define success. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now
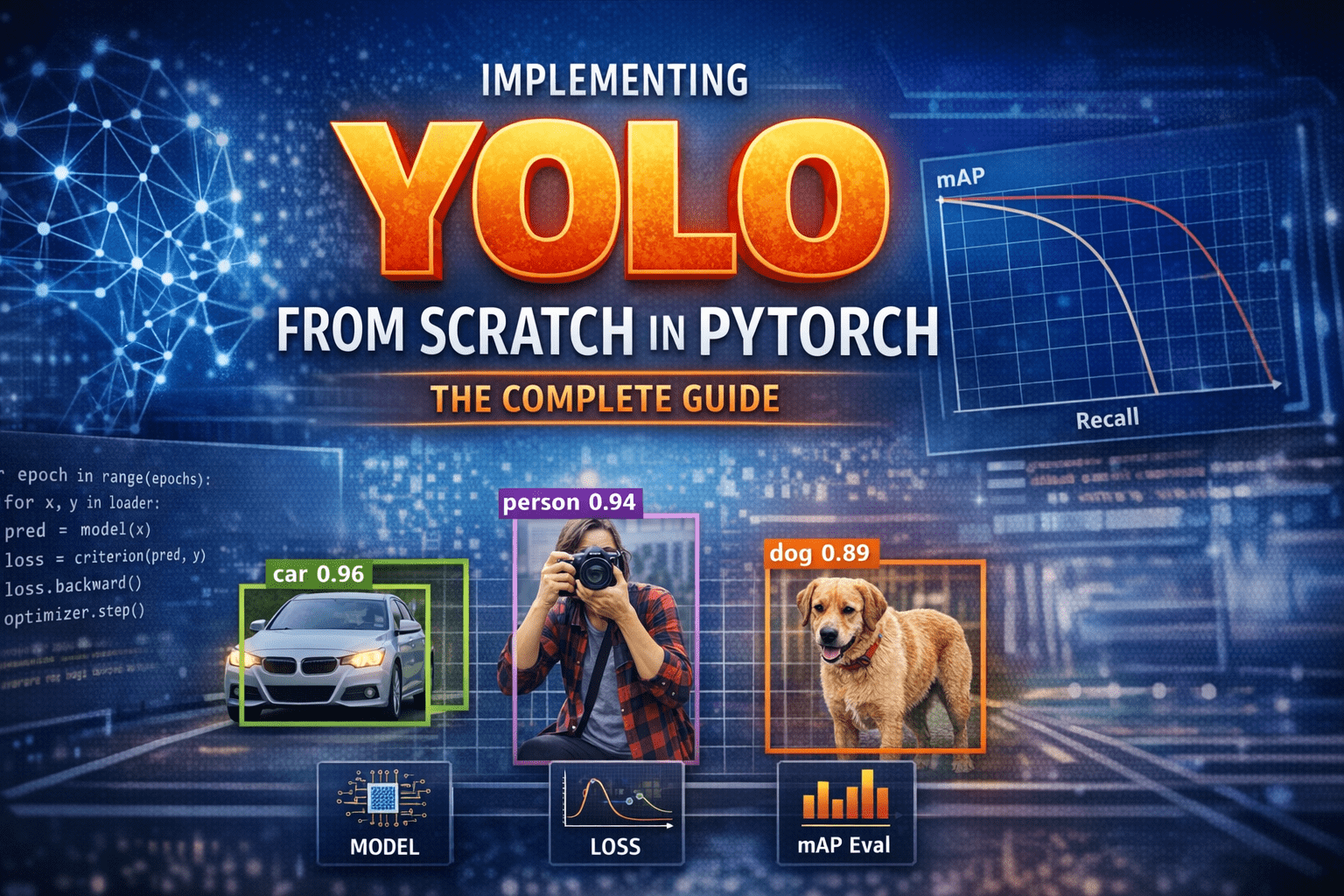
Introduction – Why YOLO Changed Everything Before YOLO, computers did not “see” the world the way humans do.Object detection systems were careful, slow, and fragmented. They first proposed regions that might contain objects, then classified each region separately. Detection worked—but it felt like solving a puzzle one piece at a time. In 2015, YOLO—You Only Look Once—introduced a radical idea: What if we detect everything in one single forward pass? Instead of multiple stages, YOLO treated detection as a single regression problem from pixels to bounding boxes and class probabilities. This guide walks through how to implement YOLO completely from scratch in PyTorch, covering: Mathematical formulation Network architecture Target encoding Loss implementation Training on COCO-style data mAP evaluation Visualization & debugging Inference with NMS Anchor-box extension 1) What YOLO means (and what we’ll build) YOLO (You Only Look Once) is a family of object detection models that predict bounding boxes and class probabilities in one forward pass. Unlike older multi-stage pipelines (proposal → refine → classify), YOLO-style detectors are dense predictors: they predict candidate boxes at many locations and scales, then filter them. There are two “eras” of YOLO-like detectors: YOLOv1-style (grid cells, no anchors): each grid cell predicts a few boxes directly. Anchor-based YOLO (YOLOv2/3 and many derivatives): each grid cell predicts offsets relative to pre-defined anchor shapes; multiple scales predict small/medium/large objects. What we’ll implement A modern, anchor-based YOLO-style detector with: Multi-scale heads (e.g., 3 scales) Anchor matching (target assignment) Loss with box regression + objectness + classification Decoding + NMS mAP evaluation COCO/custom dataset training support We’ll keep the architecture understandable rather than exotic. You can later swap in a bigger backbone easily. 2) Bounding box formats and coordinate systems You must be consistent. Most training bugs come from box format confusion. Common box formats: XYXY: (x1, y1, x2, y2) top-left & bottom-right XYWH: (cx, cy, w, h) center and size Normalized: coordinates in [0, 1] relative to image size Absolute: pixel coordinates Recommended internal convention Store dataset annotations as absolute XYXY in pixels. Convert to normalized only if needed, but keep one standard. Why XYXY is nice: Intersection/union is straightforward. Clamping to image bounds is simple. 3) IoU, GIoU, DIoU, CIoU IoU (Intersection over Union) is the standard overlap metric: IoU=∣A∩B∣/∣A∪B∣ But IoU has a problem: if boxes don’t overlap, IoU = 0, gradient can be weak. Modern detectors often use improved regression losses: GIoU: adds penalty for non-overlapping boxes based on smallest enclosing box DIoU: penalizes center distance CIoU: DIoU + aspect ratio consistency Practical rule: If you want a strong default: CIoU for box regression. If you want simpler: GIoU works well too. We’ll implement IoU + CIoU (with safe numerics). 4) Anchor-based YOLO: grids, anchors, predictions A YOLO head predicts at each grid location. Suppose a feature map is S x S (e.g., 80×80). Each cell can predict A anchors (e.g., 3). For each anchor, prediction is: Box offsets: tx, ty, tw, th Objectness logit: to Class logits: tc1..tcC So tensor shape per scale is:(B, A*(5+C), S, S) or (B, A, S, S, 5+C) after reshaping. How offsets become real boxes A common YOLO-style decode (one of several valid variants): bx = (sigmoid(tx) + cx) / S by = (sigmoid(ty) + cy) / S bw = (anchor_w * exp(tw)) / img_w (or normalized by S) bh = (anchor_h * exp(th)) / img_h Where (cx, cy) is the integer grid coordinate. Important: Your encode/decode must match your target assignment encoding. 5) Dataset preparation Annotation formats Your custom dataset can be: COCO JSON Pascal VOC XML YOLO txt (class cx cy w h normalized) We’ll support a generic internal representation: Each sample returns: image: Tensor [3, H, W] targets: Tensor [N, 6] with columns: [class, x1, y1, x2, y2, image_index(optional)] Augmentations For object detection, augmentations must transform boxes too: Resize / letterbox Random horizontal flip Color jitter Random affine (optional) Mosaic/mixup (advanced; optional) To keep this guide implementable without fragile geometry, we’ll do: resize/letterbox random flip HSV jitter (optional) 6) Building blocks: Conv-BN-Act, residuals, necks A clean baseline module: Conv2d -> BatchNorm2d -> SiLUSiLU (a.k.a. Swish) is common in YOLOv5-like families; LeakyReLU is common in YOLOv3. We can optionally add residual blocks for a stronger backbone, but even a small backbone can work to validate the pipeline. 7) Model design A typical structure: Backbone: extracts feature maps at multiple strides (8, 16, 32) Neck: combines features (FPN / PAN) Head: predicts detection outputs per scale We’ll implement a lightweight backbone that produces 3 feature maps and a simple FPN-like neck. 8) Decoding predictions At inference: Reshape outputs per scale to (B, A, S, S, 5+C) Apply sigmoid to center offsets + objectness (and often class probs) Convert to XYXY in pixel coordinates Flatten all scales into one list of candidate boxes Filter by confidence threshold Apply NMS per class (or class-agnostic NMS) 9) Target assignment (matching GT to anchors) This is the heart of anchor-based YOLO. For each ground-truth box: Determine which scale(s) should handle it (based on size / anchor match). For the chosen scale, compute IoU between GT box size and each anchor size (in that scale’s coordinate system). Select best anchor (or top-k anchors). Compute the grid cell index from the GT center. Fill the target tensors at [anchor, gy, gx] with: box regression targets objectness = 1 class target Encoding regression targets If using decode: bx = (sigmoid(tx) + cx)/Sthen target for tx is sigmoid^-1(bx*S – cx) but that’s messy. Instead, YOLO-style training often directly supervises: tx_target = bx*S – cx (a value in [0,1]) and trains with BCE on sigmoid output, or MSE on raw. tw_target = log(bw / anchor_w) (in pixels or normalized units) We’ll implement a stable variant: predict pxy = sigmoid(tx,ty) and supervise pxy with BCE/MSE to match fractional offsets predict pwh = exp(tw,th)*anchor and supervise with CIoU on decoded boxes (recommended) That’s simpler: do regression loss on decoded boxes, not on tw/th directly. 10) Loss functions YOLO-style loss usually has: Box loss: CIoU/GIoU between predicted
Introduction Before YOLO, computers didn’t see the world the way humans do. They inspected it slowly, cautiously, one object proposal at a time. Object detection worked, but it was fragmented, computationally expensive, and far from real time. Then, in 2015, a single paper changed everything. “You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection” by Joseph Redmon et al. introduced YOLOv1, a model that redefined how machines perceive images. It wasn’t just an incremental improvement, it was a conceptual revolution. This is the story of how YOLOv1 was born, how it worked, and why its impact still echoes across modern computer vision systems today. Object Detection Before YOLO: A Fragmented World Before YOLOv1, object detection research was dominated by complex pipelines stitched together from multiple independent components. Each component worked reasonably well on its own, but the overall system was fragile, slow, and difficult to optimize. The Classical Detection Pipeline A typical object detection system before 2015 looked like this: Hand-crafted or heuristic-based region proposal Selective Search Edge Boxes Sliding windows (earlier methods) Feature extraction CNN features (AlexNet, VGG, etc.) Run separately on each proposed region Classification SVMs or softmax classifiers One classifier per region Bounding box regression Fine-tuning box coordinates post-classification Each stage was trained independently, often with different objectives. Why This Was a Problem Redundant computationThe same image features were recomputed hundreds of times. No global contextThe model never truly “saw” the full image at once. Pipeline fragilityErrors in region proposals could never be recovered downstream. Poor real-time performanceEven Fast R-CNN struggled to exceed a few FPS. Object detection worked, but it felt like a workaround, not a clean solution. The YOLO Philosophy: Detection as a Single Learning Problem YOLOv1 challenged the dominant assumption that object detection must be a multi-stage problem. Instead, it asked a radical question: Why not predict everything at once, directly from pixels? A Conceptual Shift YOLO reframed object detection as: A single regression problem from image pixels to bounding boxes and class probabilities. This meant: No region proposals No sliding windows No separate classifiers No post-hoc stitching Just one neural network, trained end-to-end. Why This Matters This shift: Simplified the learning objective Reduced engineering complexity Allowed gradients to flow across the entire detection task Enabled true real-time inference YOLO didn’t just optimize detection, it redefined what detection was. How YOLOv1 Works: A New Visual Grammar YOLOv1 introduced a structured way for neural networks to “describe” an image. Grid-Based Responsibility Assignment The image is divided into an S × S grid (commonly 7 × 7). Each grid cell: Is responsible for objects whose center lies within it Predicts bounding boxes and class probabilities This created a spatial prior that helped the network reason about where objects tend to appear. Bounding Box Prediction Details Each grid cell predicts B bounding boxes, where each box consists of: x, y → center coordinates (relative to the grid cell) w, h → width and height (relative to the image) confidence score The confidence score encodes: Pr(object) × IoU(predicted box, ground truth) This was clever, it forced the network to jointly reason about objectness and localization quality. Class Prediction Strategy Instead of predicting classes per bounding box, YOLOv1 predicted: One set of class probabilities per grid cell This reduced complexity but introduced limitations in crowded scenes, a trade-off YOLOv1 knowingly accepted. YOLOv1 Architecture: Designed for Global Reasoning YOLOv1’s network architecture was intentionally designed to capture global image context. Architecture Breakdown 24 convolutional layers 2 fully connected layers Inspired by GoogLeNet (but simpler) Pretrained on ImageNet classification The final fully connected layers allowed YOLO to: Combine spatially distant features Understand object relationships Avoid false positives caused by local texture patterns Why Global Context Matters Traditional detectors often mistook: Shadows for objects Textures for meaningful regions YOLO’s global reasoning reduced these errors by understanding the scene as a whole. The YOLOv1 Loss Function: Balancing Competing Objectives Training YOLOv1 required solving a delicate optimization problem. Multi-Part Loss Components YOLOv1’s loss function combined: Localization loss Errors in x, y, w, h Heavily weighted to prioritize accurate boxes Confidence loss Penalized incorrect objectness predictions Classification loss Penalized wrong class predictions Smart Design Choices Higher weight for bounding box regression Lower weight for background confidence Square root applied to width and height to stabilize gradients These design choices directly influenced how future detection losses were built. Speed vs Accuracy: A Conscious Design Trade-Off YOLOv1 was explicit about its priorities. YOLO’s Position Slightly worse localization is acceptable if it enables real-time vision. Performance Impact YOLOv1 ran an order of magnitude faster than competing detectors Enabled deployment on: Live camera feeds Robotics systems Embedded devices (with Fast YOLO) This trade-off reshaped how researchers evaluated detection systems, not just by accuracy, but by usability. Where YOLOv1 Fell Short, and Why That’s Important YOLOv1’s limitations weren’t accidental; they revealed deep insights. Small Objects Grid resolution limited detection granularity Small objects often disappeared within grid cells Crowded Scenes One object class prediction per cell Overlapping objects confused the model Localization Precision Coarse bounding box predictions Lower IoU scores than region-based methods Each weakness became a research question that drove YOLOv2, YOLOv3, and beyond. Why YOLOv1 Changed Computer Vision Forever YOLOv1 didn’t just introduce a model, it introduced a mindset. End-to-End Learning as a Principle Detection systems became: Unified Differentiable Easier to deploy and optimize Real-Time as a First-Class Metric After YOLO: Speed was no longer optional Real-time inference became an expectation A Blueprint for Future Detectors Modern architectures, CNN-based and transformer-based alike, inherit YOLO’s core ideas: Dense prediction Single-pass inference Deployment-aware design Final Reflection: The Day Detection Became Vision YOLOv1 marked the moment when object detection stopped being a patchwork of tricks and became a coherent vision system. It taught the field that: Seeing fast unlocks new realities Simplicity scales End-to-end learning changes how machines understand the world YOLO didn’t just look once. It made computer vision see differently forever. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec
Introduction Data annotation is often described as the “easy part” of artificial intelligence. Draw a box, label an image, tag a sentence, done. In reality, data annotation is one of the most underestimated, labor-intensive, and intellectually demanding stages of any AI system. Many modern AI failures can be traced not to weak models, but to weak or inconsistent annotation. This article explores why data annotation is far more complex than it appears, what makes it so critical, and how real-world experience exposes its hidden challenges. 1. Annotation Is Not Mechanical Work At first glance, annotation looks like repetitive manual labor. In practice, every annotation is a decision. Even simple tasks raise difficult questions: Where exactly does an object begin and end? Is this object partially occluded or fully visible? Does this text express sarcasm or literal meaning? Is this medical structure normal or pathological? These decisions require context, judgment, and often domain knowledge. Two annotators can look at the same data and produce different “correct” answers, both defensible and both problematic for model training. 2. Ambiguity Is the Default, Not the Exception Real-world data is messy by nature. Images are blurry, audio is noisy, language is vague, and human behavior rarely fits clean categories. Annotation guidelines attempt to reduce ambiguity, but they can never eliminate it. Edge cases appear constantly: Is a pedestrian behind glass still a pedestrian? Does a cracked bone count as fractured or intact? Is a social media post hate speech or quoted hate speech? Every edge case forces annotators to interpret intent, context, and consequences, something no checkbox can fully capture. 3. Quality Depends on Consistency, Not Just Accuracy A single correct annotation is not enough. Models learn patterns across millions of examples, which means consistency matters more than individual brilliance. Problems arise when: Guidelines are interpreted differently across teams Multiple vendors annotate the same dataset Annotation rules evolve mid-project Cultural or linguistic differences affect judgment Inconsistent annotation introduces noise that models quietly absorb, leading to unpredictable behavior in production. The model does not know which annotator was “right”. It only knows patterns. 3. Quality Depends on Consistency, Not Just Accuracy A single correct annotation is not enough. Models learn patterns across millions of examples, which means consistency matters more than individual brilliance. Problems arise when: Guidelines are interpreted differently across teams Multiple vendors annotate the same dataset Annotation rules evolve mid-project Cultural or linguistic differences affect judgment Inconsistent annotation introduces noise that models quietly absorb, leading to unpredictable behavior in production. The model does not know which annotator was “right”. It only knows patterns. 5. Scale Introduces New Problems As annotation projects grow, complexity compounds: Thousands of annotators Millions of samples Tight deadlines Continuous dataset updates Maintaining quality at scale requires audits, consensus scoring, gold standards, retraining, and constant feedback loops. Without this infrastructure, annotation quality degrades silently while costs continue to rise. 6. The Human Cost Is Often Ignored Annotation is cognitively demanding and, in some cases, emotionally exhausting. Content moderation, medical data, accident footage, or sensitive text can take a real psychological toll. Yet annotation work is frequently undervalued, underpaid, and invisible. This leads to high turnover, rushed decisions, and reduced quality, directly impacting AI performance. 7. A Real Experience from the Field “At the beginning, I thought annotation was just drawing boxes,” says Ahmed, a data annotator who worked on a medical imaging project for over two years. “After the first week, I realized every image was an argument. Radiologists disagreed with each other. Guidelines changed. What was ‘correct’ on Monday was ‘wrong’ by Friday.” He explains that the hardest part was not speed, but confidence. “You’re constantly asking yourself: am I helping the model learn the right thing, or am I baking in confusion? When mistakes show up months later in model evaluation, you don’t even know which annotation caused it.” For Ahmed, annotation stopped being a task and became a responsibility. “Once you understand that models trust your labels blindly, you stop calling it simple work.” 8. Why This Matters More Than Ever As AI systems move into healthcare, transportation, education, and governance, annotation quality becomes a foundation issue. Bigger models cannot compensate for unclear or biased labels. More data does not fix inconsistent data. The industry’s focus on model size and architecture often distracts from a basic truth:AI systems are only as good as the data they are taught to trust. Conclusion Data annotation is not a preliminary step. It is core infrastructure. It demands judgment, consistency, domain expertise, and human care. Calling it “simple” minimizes the complexity of real-world data and the people who shape it. The next time an AI system fails in an unexpected way, the answer may not be in the model at all, but in the labels it learned from. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Introduction When people hear “AI-powered driving,” many instinctively think of Large Language Models (LLMs). After all, LLMs can write essays, generate code, and argue philosophy at 2 a.m. But putting a car safely through a busy intersection is a very different problem. Waymo, Google’s autonomous driving company, operates far beyond the scope of LLMs. Its vehicles rely on a deeply integrated robotics and AI stack, combining sensors, real-time perception, probabilistic reasoning, and control systems that must work flawlessly in the physical world, where mistakes are measured in metal, not tokens. In short: Waymo doesn’t talk its way through traffic. It computes its way through it. The Big Picture: The Waymo Autonomous Driving Stack Waymo’s system can be understood as a layered pipeline: Sensing the world Perceiving and understanding the environment Predicting what will happen next Planning safe and legal actions Controlling the vehicle in real time Each layer is specialized, deterministic where needed, probabilistic where required, and engineered for safety, not conversation. 1. Sensors: Seeing More Than Humans Can Waymo vehicles are packed with redundant, high-resolution sensors. This is the foundation of everything. Key Sensor Types LiDAR: Creates a precise 3D map of the environment using laser pulses. Essential for depth and shape understanding. Cameras: Capture color, texture, traffic lights, signs, and human gestures. Radar: Robust against rain, fog, and dust; excellent for detecting object velocity. Audio & IMU sensors: Support motion tracking and system awareness. Unlike humans, Waymo vehicles see 360 degrees, day and night, without blinking or getting distracted by billboards. 2. Perception: Turning Raw Data Into Reality Sensors alone are just noisy streams of data. Perception is where AI earns its keep. What Perception Does Detects objects: cars, pedestrians, cyclists, animals, cones Classifies them: vehicle type, posture, motion intent Tracks them over time in 3D space Understands road geometry: lanes, curbs, intersections This layer relies heavily on computer vision, sensor fusion, and deep neural networks, trained on millions of real-world and simulated scenarios. Importantly, this is not text-based reasoning. It is spatial, geometric, and continuous, things LLMs are fundamentally bad at. 3. Prediction: Anticipating the Future (Politely) Driving isn’t about reacting; it’s about predicting. Waymo’s prediction systems estimate: Where nearby agents are likely to move Multiple possible futures, each with probabilities Human behaviors like hesitation, aggression, or compliance For example, a pedestrian near a crosswalk isn’t just a “person.” They’re a set of possible trajectories with likelihoods attached. This probabilistic modeling is critical, and again, very different from next-word prediction in LLMs. 4. Planning: Making Safe, Legal, and Social Decisions Once the system understands the present and predicts the future, it must decide what to do. Planning Constraints Traffic laws Safety margins Passenger comfort Road rules and local norms The planner evaluates thousands of possible maneuvers, lane changes, stops, turns, and selects the safest viable path. This process involves optimization algorithms, rule-based logic, and learned models, not free-form language generation. There is no room for “creative interpretation” when a red light is involved. 5. Control: Executing With Precision Finally, the control system translates plans into: Steering angles Acceleration and braking Real-time corrections These controls operate at high frequency (milliseconds), reacting instantly to changes. This is classical robotics and control theory territory, domains where determinism beats eloquence every time. Where LLMs Fit (and Where They Don’t) LLMs are powerful, but Waymo’s core driving system does not depend on them. LLMs May Help With: Human–machine interaction Customer support Natural language explanations Internal tooling and documentation LLMs Are Not Used For: Real-time driving decisions Safety-critical control Sensor fusion or perception Vehicle motion planning Why? Because LLMs are: Non-deterministic Hard to formally verify Prone to confident errors (a.k.a. hallucinations) A car that hallucinates is not a feature. The Bigger Picture: Democratizing Medical AI Healthcare inequality is not just about access to doctors, it is about access to knowledge. Open medical AI models: Lower barriers for low-resource regions Enable local innovation Reduce dependence on external vendors If used responsibly, MedGemma could help ensure that medical AI benefits are not limited to the few who can afford them. Simulation: Where Waymo Really Scales One of Waymo’s biggest advantages is simulation. Billions of miles driven virtually Rare edge cases replayed thousands of times Synthetic scenarios that would be unsafe to test in reality Simulation allows Waymo to validate improvements before deployment and measure safety statistically—something no human-only driving system can do. Safety and Redundancy: The Unsexy Superpower Waymo’s system is designed with: Hardware redundancy Software fail-safes Conservative decision policies Continuous monitoring If something is uncertain, the car slows down or stops. No bravado. No ego. Just math. Conclusion: Beyond Language, Into Reality Waymo works because it treats autonomous driving as a robotics and systems engineering problem, not a conversational one. While LLMs dominate headlines, Waymo quietly solves one of the hardest real-world AI challenges: safely navigating unpredictable human environments at scale. In other words, LLMs may explain traffic laws beautifully, but Waymo actually follows them. And on the road, that matters more than sounding smart. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Introduction Artificial intelligence has been circling healthcare for years, diagnosing images, summarizing clinical notes, predicting risks, yet much of its real power has remained locked behind proprietary walls. Google’s MedGemma changes that equation. By releasing open medical AI models built specifically for healthcare contexts, Google is signaling a shift from “AI as a black box” to AI as shared infrastructure for medicine. This is not just another model release. MedGemma represents a structural change in how healthcare AI can be developed, validated, and deployed. The Problem With Healthcare AI So Far Healthcare AI has faced three persistent challenges: OpacityMany high-performing medical models are closed. Clinicians cannot inspect them, regulators cannot fully audit them, and researchers cannot adapt them. General Models, Specialized RisksLarge general-purpose language models are not designed for clinical nuance. Small mistakes in medicine are not “edge cases”, they are liability. Inequitable AccessAdvanced medical AI often ends up concentrated in large hospitals, well-funded startups, or high-income countries. The result is a paradox: AI shows promise in healthcare, but trust, scalability, and equity remain unresolved. What Is MedGemma? MedGemma is a family of open-weight medical AI models released by Google, built on the Gemma architecture but adapted specifically for healthcare and biomedical use cases. Key characteristics include: Medical-domain tuning (clinical language, biomedical concepts) Open weights, enabling inspection, fine-tuning, and on-prem deployment Designed for responsible use, with explicit positioning as decision support, not clinical authority In simple terms: MedGemma is not trying to replace doctors. It is trying to become a reliable, transparent assistant that developers and institutions can actually trust. Why “Open” Matters More in Medicine Than Anywhere Else In most consumer applications, closed models are an inconvenience. In healthcare, they are a risk. Transparency and Auditability Open models allow: Independent evaluation of bias and failure modes Regulatory scrutiny Reproducible research This aligns far better with medical ethics than “trust us, it works.” Customization for Real Clinical Settings Hospitals differ. So do patient populations. Open models can be fine-tuned for: Local languages Regional disease prevalence Institutional workflows Closed APIs cannot realistically offer this depth of adaptation. Data Privacy and Sovereignty With MedGemma, organizations can: Run models on-premises Keep patient data inside institutional boundaries Comply with strict data protection regulations For healthcare systems, this is not optional, it is mandatory. Potential Use Cases That Actually Make Sense MedGemma is not a silver bullet, but it enables realistic, high-impact applications: 1. Clinical Documentation Support Drafting summaries from structured notes Translating between clinical and patient-friendly language Reducing physician burnout (quietly, which is how doctors prefer it) 2. Medical Education and Training Interactive case simulations Question-answering grounded in medical terminology Localized medical training tools in under-resourced regions 3. Research Acceleration Literature review assistance Hypothesis exploration Data annotation support for medical datasets 4. Decision Support (Not Decision Making) Flagging potential issues Surfacing relevant guidelines Assisting, not replacing, clinical judgment The distinction matters. MedGemma is positioned as a copilot, not an autopilot. Safety, Responsibility, and the Limits of AI Google has been explicit about one thing: MedGemma is not a diagnostic authority. This is important for two reasons: Legal and Ethical RealityMedicine requires accountability. AI cannot be held accountable, people can. Trust Through ConstraintModels that openly acknowledge their limits are more trustworthy than those that pretend omniscience. MedGemma’s real value lies in supporting human expertise, not competing with it. How MedGemma Could Shift the Healthcare AI Landscape From Products to Platforms Instead of buying opaque AI tools, hospitals can build their own systems on top of open foundations. From Vendor Lock-In to Ecosystems Researchers, startups, and institutions can collaborate on improvements rather than duplicating effort behind closed doors. From “AI Hype” to Clinical Reality Open evaluation encourages realistic benchmarking, failure analysis, and incremental improvement, exactly how medicine advances. The Bigger Picture: Democratizing Medical AI Healthcare inequality is not just about access to doctors, it is about access to knowledge. Open medical AI models: Lower barriers for low-resource regions Enable local innovation Reduce dependence on external vendors If used responsibly, MedGemma could help ensure that medical AI benefits are not limited to the few who can afford them. Final Thoughts Google’s MedGemma is not revolutionary because it is powerful. It is revolutionary because it is open, medical-first, and constrained by responsibility. In a field where trust matters more than raw capability, that may be exactly what healthcare AI needs. The real transformation will not come from AI replacing clinicians, but from clinicians finally having AI they can understand, adapt, and trust. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
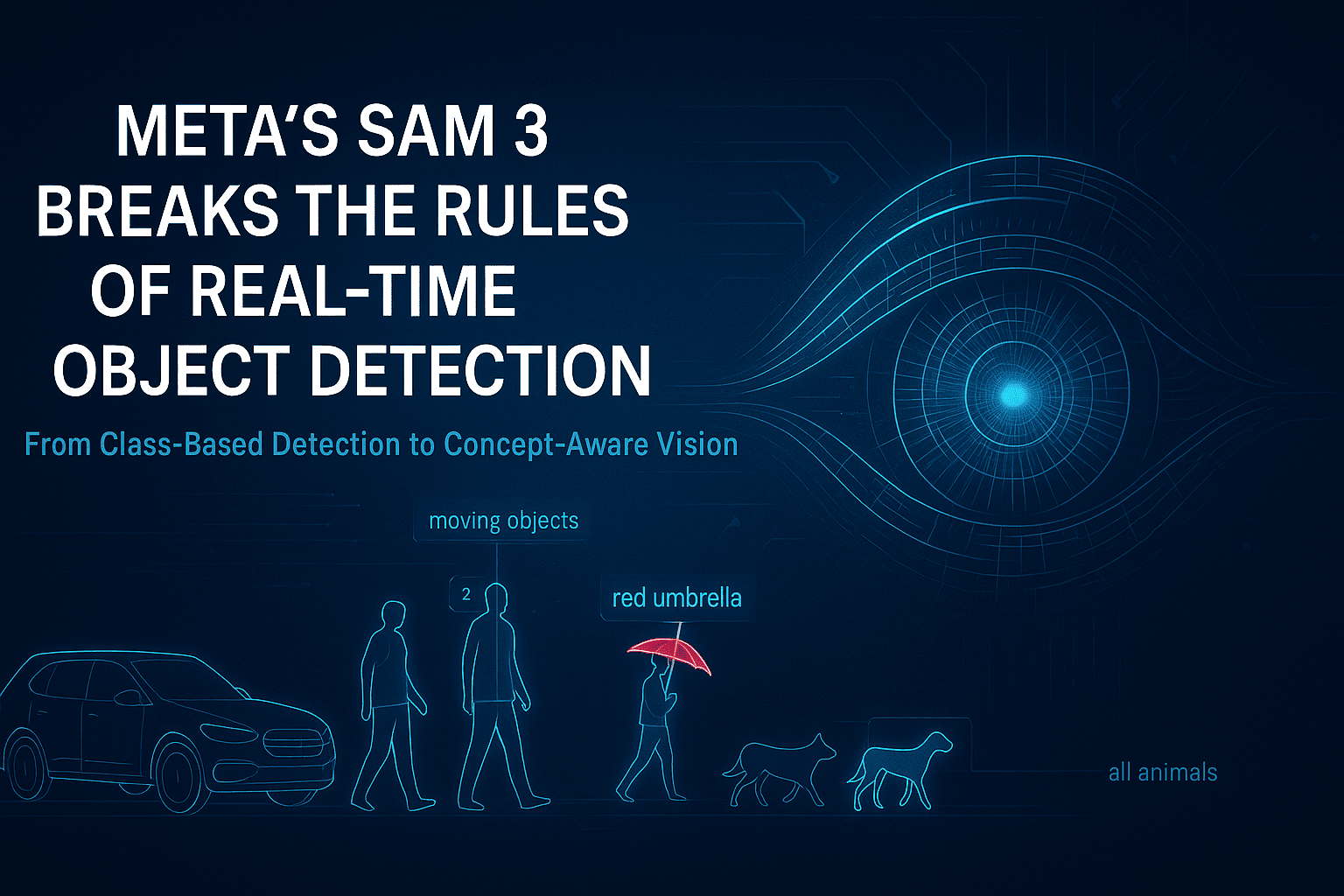
Introduction For years, real-time object detection has followed the same rigid blueprint: define a closed set of classes, collect massive labeled datasets, train a detector, bolt on a segmenter, then attach a tracker for video. This pipeline worked—but it was fragile, expensive, and fundamentally limited. Any change in environment, object type, or task often meant starting over. Meta’s Segment Anything Model 3 (SAM 3) breaks this cycle entirely. As described in the Coding Nexus analysis, SAM 3 is not just an improvement in accuracy or speed—it is a structural rethinking of how object detection, segmentation, and tracking should work in modern computer vision systems . SAM 3 replaces class-based detection with concept-based understanding, enabling real-time segmentation and tracking using simple natural-language prompts. This shift has deep implications across robotics, AR/VR, video analytics, dataset creation, and interactive AI systems. 1. The Core Problem With Traditional Object Detection Before understanding why SAM 3 matters, it’s important to understand what was broken. 1.1 Rigid Class Definitions Classic detectors (YOLO, Faster R-CNN, SSD) operate on a fixed label set. If an object category is missing—or even slightly redefined—the model fails. “Dog” might work, but “small wet dog lying on the floor” does not. 1.2 Fragmented Pipelines A typical real-time vision system involves: A detector for bounding boxes A segmenter for pixel masks A tracker for temporal consistency Each component has its own failure modes, configuration overhead, and performance tradeoffs. 1.3 Data Dependency Every new task requires new annotations. Collecting and labeling data often costs more than training the model itself. SAM 3 directly targets all three issues. 2. SAM 3’s Conceptual Breakthrough: From Classes to Concepts The most important innovation in SAM 3 is the move from class-based detection to concept-based segmentation. Instead of asking: “Is there a car in this image?” SAM 3 answers: “Show me everything that matches this concept.” That concept can be expressed as: a short text phrase a descriptive noun group or a visual example This approach is called Promptable Concept Segmentation (PCS) . Why This Matters Concepts are open-ended No retraining is required The same model works across images and videos Semantic understanding replaces rigid taxonomy This fundamentally changes how humans interact with vision systems. 3. Unified Detection, Segmentation, and Tracking SAM 3 eliminates the traditional multi-stage pipeline. What SAM 3 Does in One Pass Detects all instances of a concept Produces pixel-accurate masks Assigns persistent identities across video frames Unlike earlier SAM versions, which segmented one object per prompt, SAM 3 returns all matching instances simultaneously, each with its own identity for tracking . This makes real-time video understanding far more robust, especially in crowded or dynamic scenes. 4. How SAM 3 Works (High-Level Architecture) While the Medium article avoids low-level math, it highlights several key architectural ideas: 4.1 Language–Vision Alignment Text prompts are embedded into the same representational space as visual features, allowing semantic matching between words and pixels. 4.2 Presence-Aware Detection SAM 3 doesn’t just segment—it first determines whether a concept exists in the scene, reducing false positives and improving precision. 4.3 Temporal Memory For video, SAM 3 maintains internal memory so objects remain consistent even when: partially occluded temporarily out of frame changing shape or scale This is why SAM 3 can replace standalone trackers. 5. Real-Time Performance Implications A key insight from the article is that real-time no longer means simplified models. SAM 3 demonstrates that: High-quality segmentation Open-vocabulary understanding Multi-object tracking can coexist in a single real-time system—provided the architecture is unified rather than modular . This redefines expectations for what “real-time” vision systems can deliver. 6. Impact on Dataset Creation and Annotation One of the most immediate consequences of SAM 3 is its effect on data pipelines. Traditional Annotation Manual labeling Long turnaround times High cost per image or frame With SAM 3 Prompt-based segmentation generates masks instantly Humans shift from labeling to verification Dataset creation scales dramatically faster This is especially relevant for industries like autonomous driving, medical imaging, and robotics, where labeled data is a bottleneck. 7. New Possibilities in Video and Interactive Media SAM 3 enables entirely new interaction patterns: Text-driven video editing Semantic search inside video streams Live AR effects based on descriptions, not predefined objects For example: “Highlight all moving objects except people.” Such instructions were impractical with classical detectors but become natural with SAM 3’s concept-based approach. 8. Comparison With Previous SAM Versions Feature SAM / SAM 2 SAM 3 Object count per prompt One All matching instances Video tracking Limited / external Native Vocabulary Implicit Open-ended Pipeline complexity Moderate Unified Real-time use Experimental Practical SAM 3 is not a refinement—it is a generational shift. 9. Current Limitations Despite its power, SAM 3 is not a silver bullet: Compute requirements are still significant Complex reasoning (multi-step instructions) requires external agents Edge deployment remains challenging without distillation However, these are engineering constraints, not conceptual ones. 10. Why SAM 3 Represents a Structural Shift in Computer Vision SAM 3 changes the role of object detection in AI systems: From rigid perception → flexible understanding From labels → language From pipelines → unified models As emphasized in the Coding Nexus article, this shift is comparable to the jump from keyword search to semantic search in NLP . Final Thoughts Meta’s SAM 3 doesn’t just improve object detection—it redefines how humans specify visual intent. By making language the interface and concepts the unit of understanding, SAM 3 pushes computer vision closer to how people naturally perceive the world. In the long run, SAM 3 is less about segmentation masks and more about a future where vision systems understand what we mean, not just what we label. Visit Our Data Annotation Service Visit Now