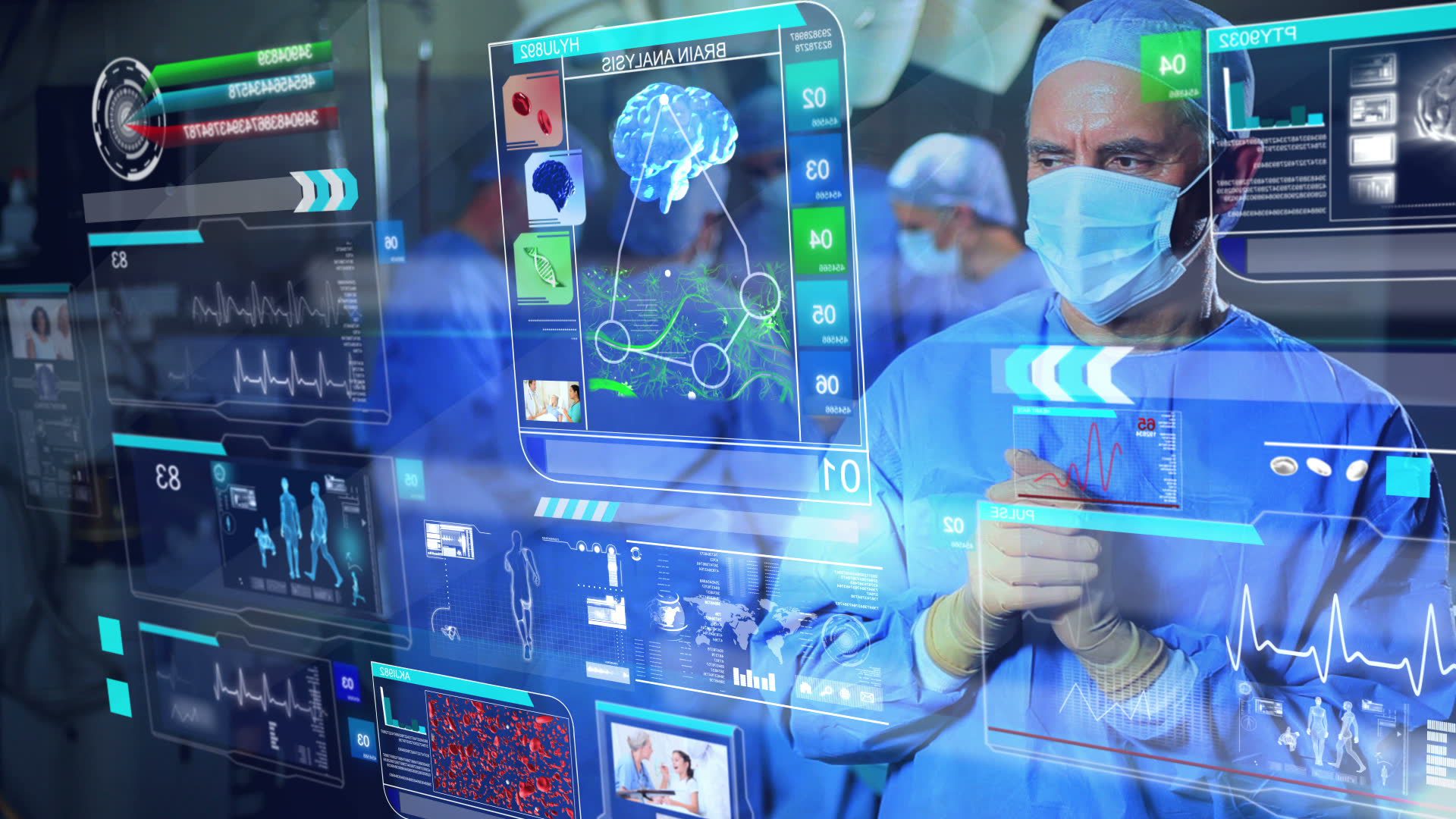
in medicine, artificial intelligence is utilized to scan medical data besides give understandings to aid get better health effects and patient encounters. Artificial intelligence (AI) is progressively becoming a component of current healthcare thanks to recent technological breakthroughs. AI is increasingly applied in medical applications for clinical decision aid and image analysis. Providers may employ clinical decision support tools to swiftly collect patient-specific information or research. Human radiologists may overlook lesions or other discoveries on CT scans, x-rays, MRIs, and other images that AI technologies evaluate. The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted numerous healthcare institutions worldwide to field-test innovative AI-powered solutions, such as algorithms meant to assist monitoring patients and COVID-19 screening tools. On is currently gathering data and defining the general guidelines for using AI in medicine. But AI’s potential to help physicians, researchers, and patients is growing [1]. There is no question that AI will play a major role in shaping and supporting contemporary medicine.
Medical AI applications
AI can improve medicine in several ways, including speeding up research and helping physicians make better judgments. Here are some uses for AI:
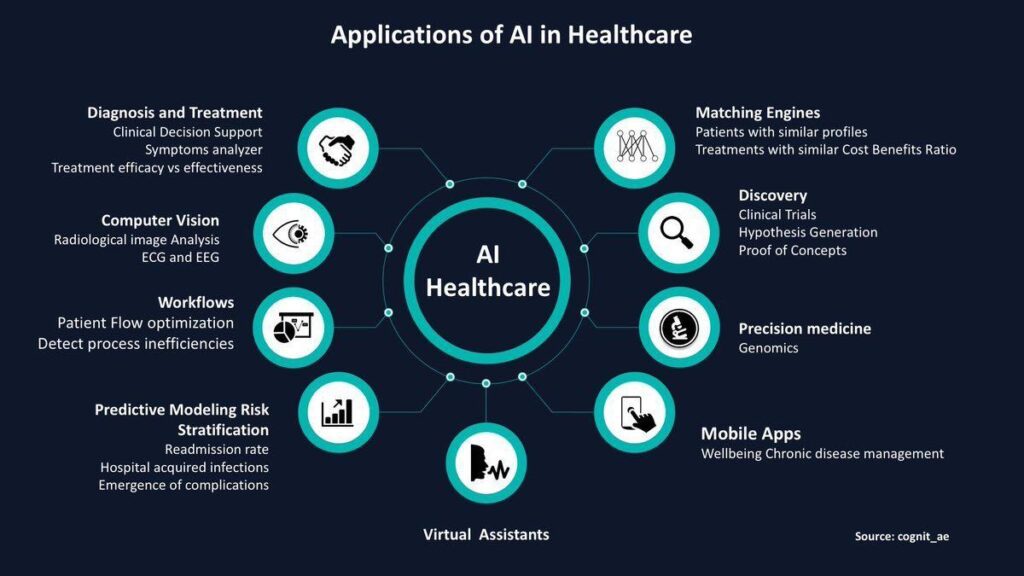
AI in medical diagnostics
AI, unlike humans, never sleeps. Machine learning algorithms might monitor critical care patients’ vital signs and inform physicians if specific risk variables rise [2]. AI can take data from medical equipment like heart monitors and seek more complicated illnesses like sepsis. One IBM customer created a predictive AI model for preterm neonates that can identify serious sepsis 75% of the time.
Personalized medicine
Precision medicine might benefit from virtual AI help. Using AI models, patients may get 24/7 tailored real-time advice since they can learn and remember their preferences. Having a virtual assistant driven by artificial intelligence that can answer questions based on a patient’s medical history, preferences, and unique needs means less information is repeated.
Medical imaging AI
AI is already used in medical imaging. Artificial neural networks driven by AI may identify indications of breast cancer and other illnesses as effectively as human radiologists. To make managing the massive quantity of medical photos easier, AI can recognize key aspects of a patient’s history and provide the relevant photographs to them, in addition to helping professionals discover early indicators of sickness.
Efficacy of trials
Encoding patient results and updating pertinent databases takes time during clinical studies. An intelligent search for medical codes may help speed up the procedure. AI reduced medical code searches by 70% for two IBM Watson Health customers.
Drug development speeded up
Part of drug development is drug discovery. Creating improved medication designs and discovering novel drug combinations are two ways AI might assist in lowering development costs. AI might help the life sciences sector address many of its big data difficulties.
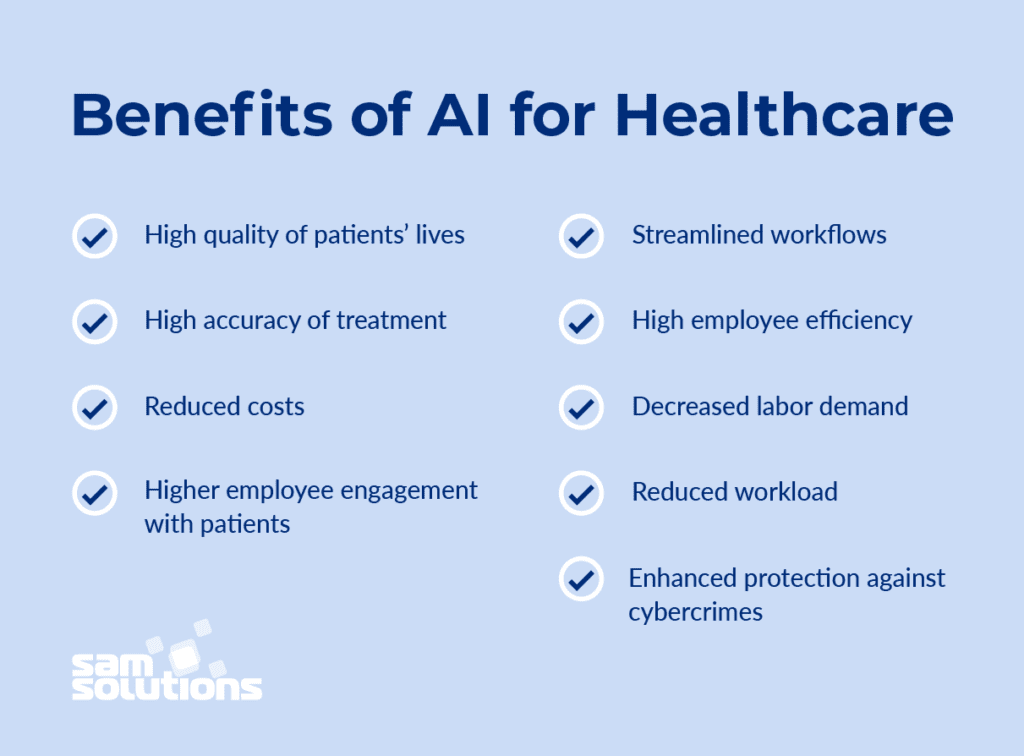
Benefits of AI in medicine
Machine learning has the potential to increase revenue opportunities for physicians and hospital staff by providing them with data-driven clinical decision support (CDS) [3]. Deep learning employs algorithms and data to provide healthcare practitioners with automatic insights. Some of the benefits are:
Patient education
Patients might benefit from improved treatment decisions if artificial intelligence (AI) is integrated into healthcare operations. Patients may benefit from trained machine learning systems that can deliver evidence-based search results while they are still in the hospital.
Easing errors
AI may assist increase patient safety in specific cases. An analysis of 53 peer-reviewed research indicated that AI-powered decision assistance systems may aid enhance mistake detection and medication management.
lowering care expenses
There are several ways AI might lower healthcare expenditures. Reduced pharmaceutical mistakes, individualized virtual health aid, fraud protection, and improved administrative and clinical processes are among the most promising prospects.
Involving doctors and patients
Many patients have inquiries after-hours. When a doctor’s office is closed, AI may assist offer 24/7 support through chatbots that answer simple queries and provide patient information. AI might also assist prioritize inquiries and highlighting material for evaluation, alerting clinicians to health issues that need further attention.
Providing context
Deep learning algorithms may utilize context to discriminate between various sorts of data. An AI system trained in natural language processing may, for example, identify which medications are appropriate based on a patient’s medical history.
References
- Steimann, F. (2001). On the use and usefulness of fuzzy sets in medical AI. Artificial intelligence in medicine, 21(1-3), 131-137.
- Muller, H., Mayrhofer, M. T., Van Veen, E. B., & Holzinger, A. (2021). The Ten Commandments of ethical medical AI. Computer, 54(07), 119-123
- Ting, D. S., Liu, Y., Burlina, P., Xu, X., Bressler, N. M., & Wong, T. Y. (2018). AI for medical imaging goes deep. Nature medicine, 24(5), 539-540.