Introduction to the Cyber Age
The digital era has ushered in unprecedented connectivity and convenience, revolutionizing the way we live, work, and communicate. However, this interconnectedness has also exposed us to a myriad of cybersecurity threats, ranging from data breaches to sophisticated cyber attacks orchestrated by malicious actors. As organizations and individuals increasingly rely on digital technologies to conduct their affairs, the need for robust cybersecurity measures has never been more critical.
In tandem with the rise of cyber threats, there has been a parallel advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. AI, encompassing disciplines such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, has emerged as a powerful tool for addressing complex problems across various domains, including cybersecurity.

Foundations of Cyber Threats
Before delving into the realm of AI-powered cybersecurity, it’s essential to establish a foundational understanding of the various cyber threats that organizations face. Cyber attacks come in many forms, ranging from common threats like phishing and malware to more sophisticated techniques such as ransomware and advanced persistent threats (APTs). By comprehensively analyzing the cyber threat landscape, organizations can better prepare themselves to defend against these evolving risks.
Case studies of notable cyber attacks provide valuable insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by threat actors. From the WannaCry ransomware attack that affected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide to the SolarWinds supply chain compromise that targeted numerous government agencies and corporations, these incidents underscore the need for proactive cybersecurity measures.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
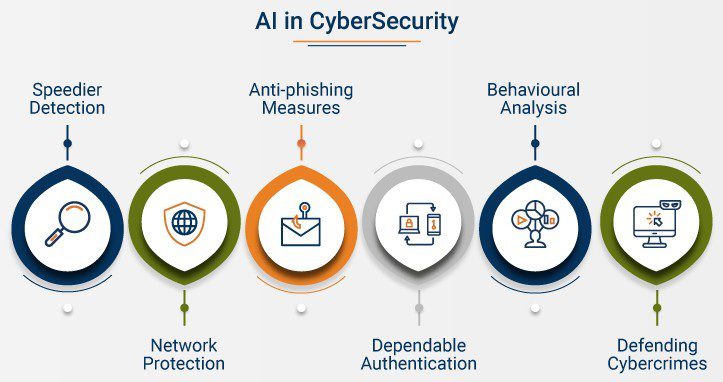
Artificial intelligence holds immense potential for transforming cybersecurity practices by augmenting human capabilities and automating repetitive tasks. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns indicative of malicious activity, enabling organizations to detect and respond to threats more effectively. Deep learning techniques, inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, excel at tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing, making them valuable tools for cybersecurity applications.
Enhancing Security with AI
One of the primary ways AI enhances cybersecurity is through threat detection and prevention. Traditional signature-based approaches to cybersecurity are limited in their ability to detect unknown or zero-day threats. In contrast, AI-powered systems can analyze behavioral patterns and anomalies to identify suspicious activity that may indicate a potential cyber attack. By continuously learning from new data and adapting to emerging threats, AI-driven security solutions can stay ahead of adversaries.
Anomaly detection is another area where AI excels. By establishing a baseline of normal behavior within an organization’s network, AI algorithms can flag deviations that may signify unauthorized access or malicious behavior. This proactive approach enables organizations to detect and mitigate security incidents before they escalate into full-blown breaches.
Behavioral analysis is a cornerstone of AI-powered cybersecurity, allowing organizations to identify subtle indicators of compromise that may evade traditional security measures. By analyzing user behavior, network traffic, and system activity, AI algorithms can identify suspicious patterns indicative of insider threats, credential misuse, or lateral movement by attackers.
Predictive analytics leverages AI and machine learning to forecast future cybersecurity threats based on historical data and current trends. By analyzing indicators of compromise and correlating disparate data sources, predictive analytics can help organizations anticipate and preemptively address emerging threats, reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
AI-Powered Defense Mechanisms
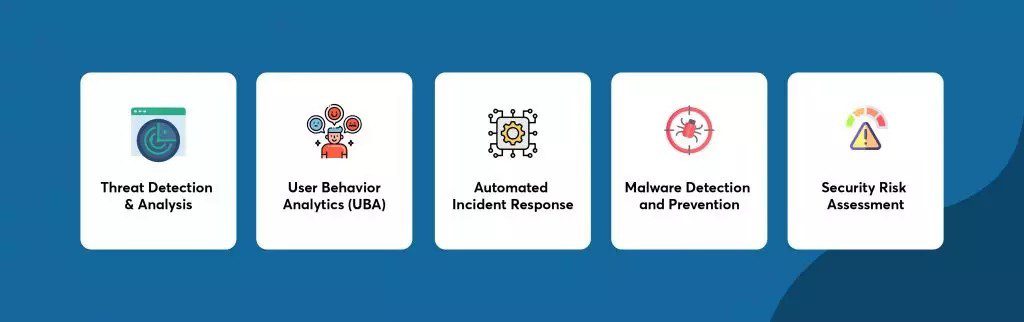
In addition to threat detection and prevention, AI plays a crucial role in developing advanced defense mechanisms to protect organizations against cyber threats. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) use AI algorithms to monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity, such as suspicious patterns or known attack signatures. By automatically blocking or mitigating potential threats in real-time, these systems help organizations maintain the integrity and availability of their networks.
Endpoint security solutions leverage AI to protect individual devices, such as computers, smartphones, and IoT devices, from cyber threats. By continuously monitoring endpoint activity and detecting anomalies indicative of malware or unauthorized access attempts, AI-powered endpoint security solutions can provide organizations with comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
Network traffic analysis utilizes AI algorithms to monitor and analyze network traffic for signs of malicious activity or anomalous behavior. By correlating network traffic data with threat intelligence feeds and security policies, AI-driven network traffic analysis solutions can identify and respond to cyber threats in real-time, minimizing the risk of data breaches or network intrusions.
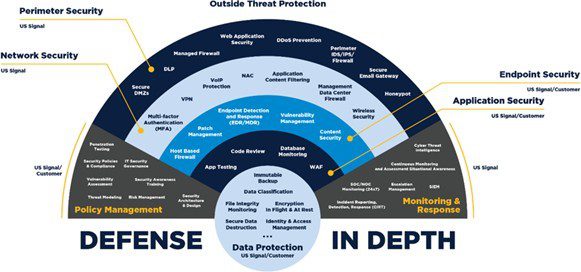
AI in Identity and Access Management
Identity and access management (IAM) is a critical component of cybersecurity, governing the authentication and authorization of users accessing organizational resources. AI technologies can enhance IAM systems by improving authentication techniques, enhancing access control mechanisms, and detecting anomalous user behavior.
Authentication techniques such as biometric authentication and behavioral biometrics leverage AI algorithms to verify the identity of users based on unique physiological or behavioral characteristics. By analyzing factors such as fingerprints, facial features, voice patterns, and typing behavior, AI-powered authentication systems can provide organizations with secure and convenient access controls.
Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC), determine the level of access granted to users based on predefined policies and rules. AI can enhance access control by dynamically adjusting access privileges in response to changes in user behavior, risk factors, or contextual information.
Privileged access management (PAM) solutions use AI to monitor and manage access to privileged accounts, which have elevated permissions and pose a significant security risk if compromised. By implementing AI-driven anomaly detection and behavioral analysis capabilities, PAM solutions can identify suspicious activity indicative of unauthorized access attempts or insider threats.
Identity governance and administration (IGA) frameworks govern the lifecycle of user identities within an organization, including the creation, management, and revocation of user accounts and access privileges. AI can streamline IGA processes by automating identity lifecycle management tasks, identifying dormant or orphaned accounts, and enforcing compliance with regulatory requirements and security policies.
Securing Cloud Infrastructures with AI
As organizations increasingly migrate their IT infrastructure to the cloud, ensuring the security of cloud-based environments has become a top priority. AI technologies can enhance cloud security by providing real-time threat detection and response capabilities, securing cloud workloads and data, and mitigating risks associated with cloud adoption.
Cloud security challenges, such as data breaches, misconfigurations, and insider threats, require comprehensive security measures to protect sensitive information and ensure regulatory compliance. AI-powered cloud security solutions can address these challenges by leveraging machine learning algorithms to monitor cloud environments for security risks, detect and respond to cyber threats, and automate security operations.
AI-based cloud security solutions encompass a range of capabilities, including cloud workload protection platforms (CWPP), cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools, and cloud access security brokers (CASB). These solutions provide organizations with visibility into their cloud infrastructure, help them identify and remediate security misconfigurations, and enforce security policies across cloud services and applications.
Cloud workload protection platforms (CWPP) use AI algorithms to monitor and protect cloud workloads, such as virtual machines, containers, and serverless applications, from cyber threats. By analyzing workload behavior and identifying indicators of compromise, CWPP solutions can detect and mitigate security risks in cloud environments, helping organizations maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and applications.
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools help organizations assess and manage the security posture of their cloud infrastructure, identifying misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance gaps that may expose them to cyber threats. By automating security assessment and remediation tasks, CSPM solutions enable organizations to proactively address security risks and ensure the security of their cloud deployments.
Cloud access security brokers (CASB) play a vital role in securing cloud applications and services by providing visibility, control, and compliance capabilities. AI-powered CASB solutions analyze cloud usage patterns, detect anomalous behavior, and enforce security policies to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Threat Intelligence and AI
Threat intelligence plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by providing organizations with timely and relevant information about emerging cyber threats, adversaries, and vulnerabilities. AI technologies can enhance threat intelligence capabilities by automating threat detection, analysis, and response, enabling organizations to stay ahead of cyber adversaries and proactively defend against emerging threats.
Threat intelligence platforms (TIPs) leverage AI algorithms to collect, correlate, and analyze vast amounts of threat data from disparate sources, such as open-source intelligence feeds, dark web forums, and security incident reports. By identifying patterns, trends, and correlations within threat data, TIPs help organizations identify emerging threats, assess their potential impact, and prioritize their response efforts.
Threat hunting is a proactive cybersecurity approach that involves actively searching for signs of compromise or malicious activity within an organization’s network. AI-driven threat hunting tools use machine learning algorithms to analyze network traffic, endpoint data, and security logs for indicators of compromise, enabling security teams to identify and mitigate threats before they cause damage.
AI-driven threat intelligence analysis capabilities enable organizations to extract actionable insights from large volumes of threat data, such as malware signatures, IP addresses, and attack patterns. By automating the process of threat analysis and enrichment, AI technologies help organizations identify relevant threats, assess their severity, and prioritize their response actions.
Threat intelligence sharing and collaboration are essential for collective defense against cyber threats, as no single organization can defend against all threats alone. AI-powered threat intelligence platforms facilitate the sharing of threat data and analysis between organizations, enabling them to collaborate on threat detection, analysis, and response efforts. By pooling their resources and expertise, organizations can improve their collective cybersecurity posture and better defend against common adversaries.
The Human Element: AI and Human Collaboration
While AI technologies hold tremendous potential for enhancing cybersecurity, they are not a panacea for all security challenges. Human expertise and judgment remain indispensable for effectively defending against cyber threats and adapting to evolving security risks. Augmented intelligence, which combines the strengths of AI and human intelligence, offers a promising approach for addressing complex cybersecurity challenges.
Human-machine teaming involves collaboration between humans and AI technologies to achieve common goals, such as threat detection, incident response, and decision-making. By leveraging AI algorithms to analyze data, identify patterns, and automate routine tasks, human operators can focus their efforts on high-level strategic activities, such as threat hunting, incident analysis, and decision-making.
Challenges and opportunities of human-AI collaboration include concerns about AI bias, transparency, and accountability, as well as the potential for AI technologies to augment human capabilities and improve cybersecurity outcomes. By fostering a culture of collaboration, trust, and continuous learning, organizations can harness the collective expertise of humans and AI technologies to effectively defend against cyber threats and adapt to changing security requirements.
Ethical and Legal Implications of AI in Cybersecurity
As AI technologies become increasingly integrated into cybersecurity practices, it is essential to consider the ethical and legal implications of their use. AI bias, privacy concerns, regulatory compliance, and accountability are among the key ethical and legal considerations that organizations must address when deploying AI-driven cybersecurity solutions.
Bias and fairness in AI algorithms can have significant implications for cybersecurity, as biased algorithms may inadvertently discriminate against certain groups or produce inaccurate results. Organizations must ensure that AI algorithms are trained on diverse and representative datasets, regularly audited for bias, and transparently documented to mitigate the risk of unintended consequences.
Privacy concerns arise from the collection, processing, and sharing of sensitive information in AI-driven cybersecurity systems. Organizations must implement privacy-preserving measures, such as data anonymization, encryption, and access controls, to protect the confidentiality and integrity of personal data and comply with privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Regulatory landscape for AI in cybersecurity is evolving, with governments and regulatory bodies introducing new laws, guidelines, and standards to govern the responsible use of AI technologies. Organizations must stay informed about relevant regulations and ensure that their AI-driven cybersecurity practices comply with legal requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
AI governance and accountability are essential for ensuring the responsible and ethical use of AI technologies in cybersecurity. Organizations must establish clear policies, procedures, and controls for the development, deployment, and monitoring of AI-driven cybersecurity solutions, as well as mechanisms for accountability, transparency, and oversight.
Future Trends and Challenges
Looking ahead, several emerging trends and challenges are shaping the future of AI in cybersecurity. Quantum computing, adversarial AI, AI for cyber resilience, and emerging threats are among the key areas of focus for cybersecurity researchers, practitioners, and policymakers.
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computing technology, with the potential to render existing cryptographic algorithms obsolete and disrupt traditional cybersecurity practices. Organizations must prepare for the advent of quantum computing by exploring post-quantum cryptography, quantum-resistant algorithms, and quantum-safe security measures.
Adversarial AI poses a growing threat to cybersecurity, as malicious actors leverage AI technologies to develop sophisticated cyber attacks that evade detection and exploit vulnerabilities in AI-driven security systems. Organizations must develop robust defenses against adversarial attacks, such as adversarial training, robustness testing, and anomaly detection techniques.
AI for cyber resilience involves using AI technologies to enhance organizations’ ability to withstand, adapt to, and recover from cyber attacks and other security incidents. By integrating AI-driven resilience capabilities into their cybersecurity strategies, organizations can improve their ability to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats, minimizing the impact on their operations and stakeholders.
Emerging threats, such as deepfakes, ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), and supply chain attacks, pose significant challenges for cybersecurity practitioners, requiring innovative approaches and collaborative efforts to address. By staying vigilant, proactive, and adaptive, organizations can effectively defend against emerging threats and safeguard their digital assets against evolving cyber risks.
Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
To reap the benefits of AI in cybersecurity, organizations must develop comprehensive strategies for AI adoption, implementation, and governance. Building AI-driven security operations centers (SOCs), investing in skills and training, and learning from successful case studies are essential steps in implementing AI in cybersecurity.
Strategies for AI adoption in cybersecurity include assessing organizational readiness, identifying use cases and business objectives, evaluating AI technologies and vendors, and developing implementation plans and roadmaps. By aligning AI initiatives with strategic priorities, organizational goals, and industry best practices, organizations can maximize the value and impact of AI in cybersecurity.
Building AI-driven SOCs involves integrating AI technologies into existing security infrastructure, processes, and workflows to enhance threat detection, response, and decision-making capabilities. By leveraging AI-powered security analytics, automation, and orchestration, SOCs can improve their ability to detect and mitigate cyber threats in real-time, reducing the time to detect and respond to security incidents.
Investing in skills and training is essential for building a workforce capable of harnessing the power of AI in cybersecurity. Organizations must provide employees with opportunities to develop expertise in AI technologies, cybersecurity principles, and relevant domains, such as data science, machine learning, and threat intelligence. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and skill development, organizations can empower their employees to effectively leverage AI in cybersecurity and drive innovation in the field.
Learning from successful case studies provides valuable insights into the practical applications of AI in cybersecurity and the benefits it can deliver to organizations. By studying real-world examples of AI-driven security solutions, best practices, and lessons learned, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement, emulate successful strategies, and avoid common pitfalls.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intersection of artificial intelligence and cybersecurity represents a transformative force in the digital age, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance security, detect threats, and mitigate risks. By harnessing the power of AI technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity posture, protect their digital assets, and safeguard against a wide range of cyber threats.
As AI continues to evolve and advance, it is essential for organizations to stay informed about the latest developments, trends, and best practices in AI-driven cybersecurity. By fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement, organizations can leverage AI technologies to address the dynamic and evolving nature of cyber threats, adapt to changing security requirements, and achieve their strategic objectives in the digital age.
“Deciphering the Cyber Frontier” serves as a comprehensive guide to AI in cybersecurity, providing readers with the knowledge, insights, and practical guidance needed to navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity in the AI era. Whether you are a cybersecurity professional, IT leader, or aspiring practitioner, this book equips you with the tools, strategies, and resources to harness the power of AI and defend against cyber threats in an increasingly interconnected world.